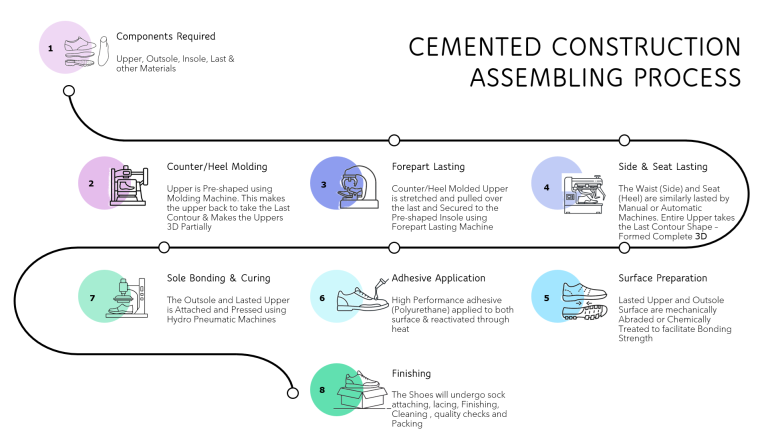
Footwear Manufacturing Insights: Adhesion & Whole Shoe Performance Testing
In professional footwear manufacturing, adhesion and whole shoe performance testing represent the final and most decisive stage of quality validation. While individual materials may pass laboratory evaluation in isolation, true product reliability can only be confirmed when the fully assembled shoe is subjected to mechanical stress, environmental exposure, and repeated deformation. For this reason, adhesion and whole shoe tests are treated as functional durability tests rather than simple compliance checks.
This article presents a deep technical examination of adhesion behaviour, bonding performance, and whole shoe testing practices commonly applied in factory laboratories and independent testing centres.
Role of Adhesion in Footwear Durability
Adhesion is the structural link that integrates dissimilar materials into a functional footwear system. Modern shoes combine rubber, EVA, PU, TPU, leather, coated textiles, and synthetic fabrics, each with different surface energies and thermal behaviour. The adhesive layer must accommodate these differences while maintaining flexibility, strength, and resistance to ageing.
Inadequate adhesion rarely causes immediate failure. Instead, problems emerge progressively during wear, appearing as edge lifting, sole separation, blistering, or internal delamination. These failures are particularly damaging because they directly affect consumer perception and brand credibility.
From a manufacturing standpoint, adhesion performance is closely tied to process stability, material compatibility, and surface preparation discipline rather than adhesive selection alone.
Adhesion Testing in Footwear Manufacturing
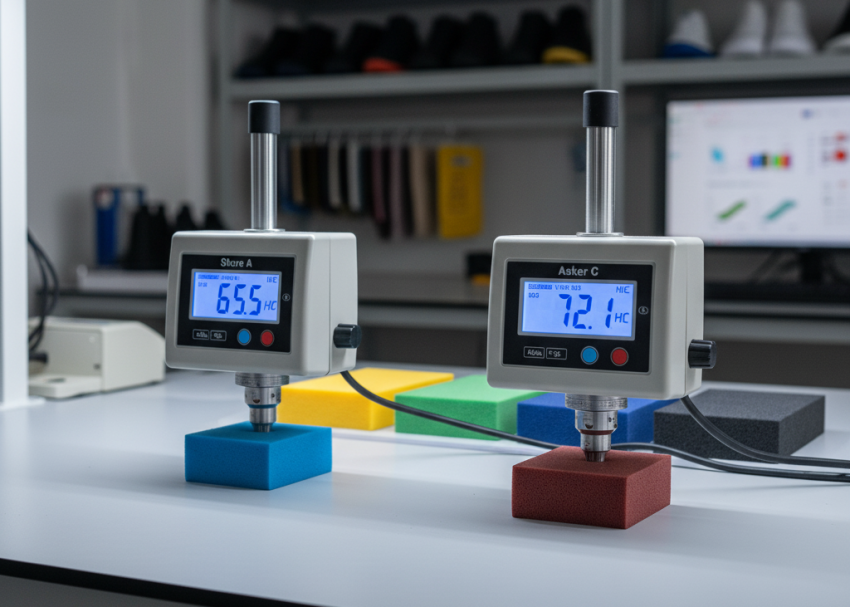
Adhesion testing evaluates the bond strength between two joined components under controlled mechanical force. These tests aim to determine whether bonded assemblies can withstand the stresses encountered during walking, flexing, and environmental exposure.
In practice, adhesion testing is carried out both before and after conditioning, as adhesive bonds are sensitive to heat, humidity, and water. Immediate post-bond results often appear satisfactory, but performance can deteriorate significantly after ageing.
Common adhesion evaluations include peel resistance, tensile separation, and shear strength measurements. Test specimens are usually prepared from finished shoes or bonded assemblies representative of production conditions.

Expert Advice: Always conduct adhesion testing after full adhesive curing and conditioning. Testing too early can mask long-term bond weakness and lead to false confidence in production stability.
Commonly Applied SATRA Test Methods : SATRA TM411 & SATRA TM401
SATRA Test Method Directory (search TM number):
🔗 https://new.satra.com/services/test-methods/test-method-list/
Factors Affecting Adhesion Performance
Adhesion strength is influenced by a combination of material, process, and environmental variables. Even when the correct adhesive system is selected, poor control of these factors can result in inconsistent bonding.
Surface preparation plays a critical role. Insufficient roughing, uneven buffing, residual dust, or contamination from oils and release agents significantly reduce bond strength. Equally important is adhesive application control, including film thickness, drying time, and activation temperature.
Process parameters such as open time, bonding pressure, and cooling rate further determine final adhesion quality. Variations in these parameters across production shifts often explain sporadic adhesion failures observed during audits or wear testing.
Pro Tip: When investigating adhesion failures, compare process parameters between shifts, not just materials. Process drift is a more common root cause than adhesive formulation issues.
Search on the SATRA Test Method Directory.
🔗 https://new.satra.com/services/test-methods/test-method-list/
Whole Shoe Performance Testing – Purpose and Scope
Whole shoe performance testing evaluates the footwear as an integrated system. Unlike component testing, these evaluations account for the interaction between materials, construction methods, and adhesive bonds under simulated wear conditions.
Whole shoe tests are typically conducted after final assembly, full curing, and a defined rest period. This ensures that results reflect real-world performance rather than short-term manufacturing conditions.
Search on the SATRA Test Method Directory.
🔗 https://new.satra.com/services/test-methods/test-method-list/
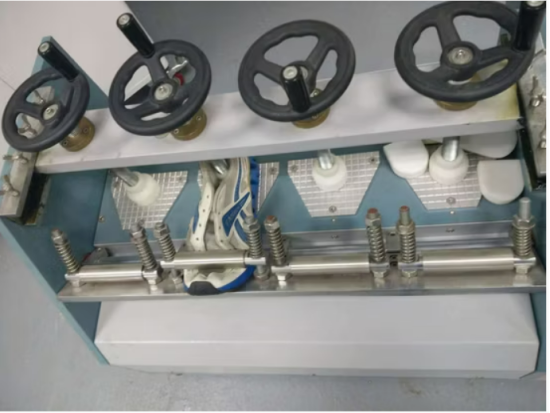

Key Whole Shoe Performance Evaluations
Flex Resistance and Fatigue Behavior
Flex testing repeatedly bends the shoe at critical flex zones to simulate walking motion. Over extended cycles, this test reveals fatigue-related failures such as sole cracking, adhesive breakdown, and upper–sole separation.
Flex resistance testing is particularly important for athletic, casual, and work footwear, where repetitive movement is unavoidable.
Reference : SATRA TM92
Search on the SATRA Test Method Directory.
🔗 https://new.satra.com/services/test-methods/test-method-list/
Sole Bond Strength in Finished Footwear
Whole shoe bond strength testing measures the force required to detach the sole from the upper after full assembly. This assessment confirms that adhesive performance remains stable when subjected to combined stresses from flexing, load, and environmental exposure.
Reference : SATRA TM411
Search on the SATRA Test Method Directory.
🔗 https://new.satra.com/services/test-methods/test-method-list/
Environmental and Water Resistance Performance
Environmental testing exposes finished footwear to water, humidity, and temperature variation. These conditions accelerate adhesive ageing and reveal weaknesses that may not appear under dry laboratory conditions.
Such testing is essential for outdoor, safety, and travel footwear, where environmental exposure is unavoidable.
Pro Tip: Always conduct adhesion and flex tests after water exposure for outdoor or casual footwear. Many adhesion failures appear only after moisture conditioning.
Reference : SATRA TM31/77
Search on the SATRA Test Method Directory.
🔗 https://new.satra.com/services/test-methods/test-method-list/
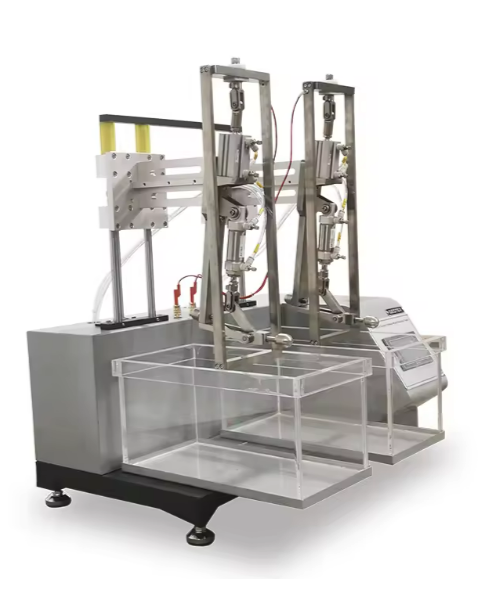

Integration into Quality Control Systems
In mature footwear manufacturing operations, adhesion and whole shoe testing are embedded into quality management systems. Testing is conducted during material approval, first-off production, periodic monitoring, and pre-shipment inspection.
Test results should remain traceable to material lots, production dates, and process conditions. This traceability enables rapid root-cause analysis when failures occur and strengthens audit readiness for global brands.
Typical Adhesion and Whole Shoe Failures
Despite structured testing, failures still arise due to process drift, inadequate ageing evaluation, or over-reliance on supplier data. The most common issues include:
- Progressive sole separation after flexing
- Adhesive softening after heat exposure
- Bond failure following water immersion
Preventive testing remains significantly more cost-effective than corrective action after shipment.
Conclusion
Adhesion and whole shoe performance testing represent the final safeguard in footwear manufacturing. When executed systematically and interpreted correctly, these tests ensure durability, functional reliability, and long-term brand trust. More importantly, they bridge the gap between laboratory validation and real-world wear expectations.
For factories and brands alike, robust adhesion and whole shoe testing is not merely a quality requirement—it is a strategic advantage.