Cemented Construction in Footwear Manufacturing: The Efficient Path to Durable Shoes
1. Introduction: Overview of Cemented Construction in Footwear
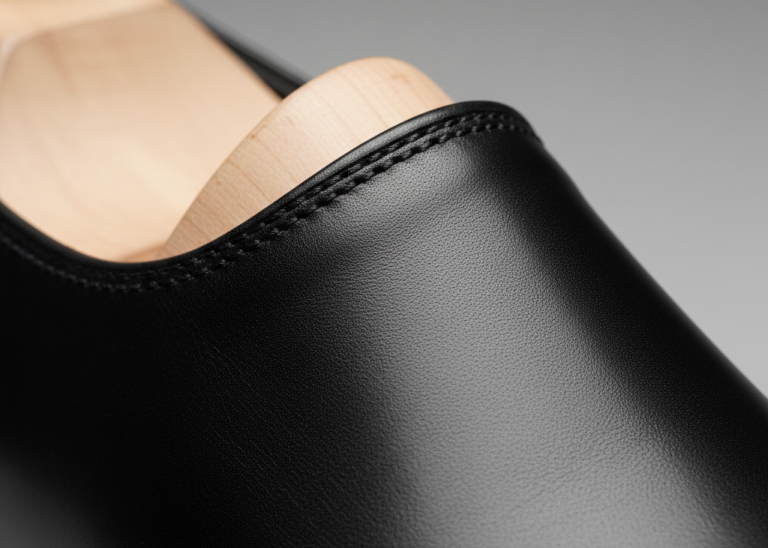
Cemented construction, also known as direct attach or lasting construction, represents one of the most widely adopted techniques in footwear manufacturing. For example, manufacturers commonly use this method for formal and casual shoes. Moreover, modern technological advancements have extended its application to sneakers and lightweight performance footwear. Because it offers efficiency, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, cemented construction has become a cornerstone of mass production in the global footwear industry. Therefore, this article examines the process, materials, and innovations associated with cemented construction in detail. It provides valuable insights for manufacturers, designers, and industry stakeholders.
2. Definition and Principles of Cemented Shoe Construction
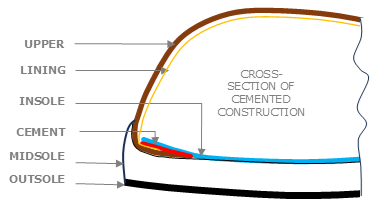
In short, cemented construction bonds the shoe upper to the sole using high-strength industrial adhesives. This approach distinguishes it from traditional stitched or welted methods that rely on sewing. As a result, the process eliminates the need for midsole stitching and creates a streamlined production approach. Furthermore, the technique uses advanced adhesive technologies to ensure a robust and durable bond. Consequently, it suits a variety of footwear types, such as mesh sneakers, leather casuals, and performance shoes. In addition, its ability to produce lightweight, flexible, and aesthetically versatile products has solidified its position as a standard practice in the footwear sector.
3. Detailed Manufacturing Process of Cemented Footwear
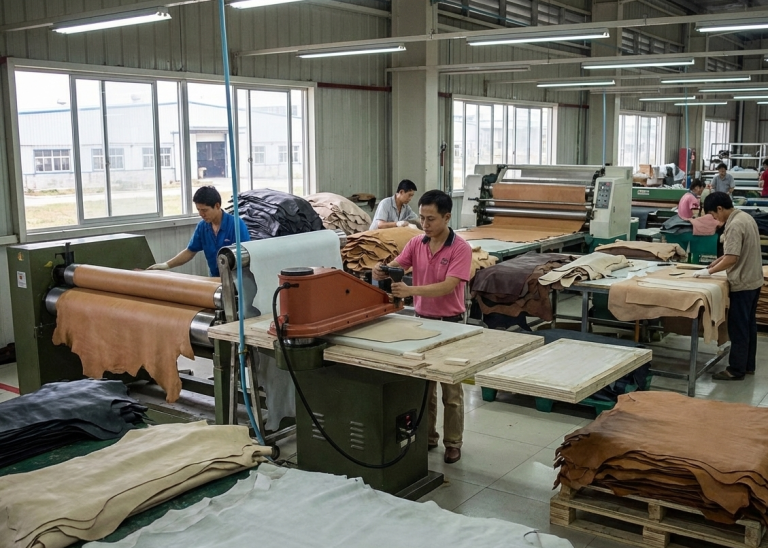
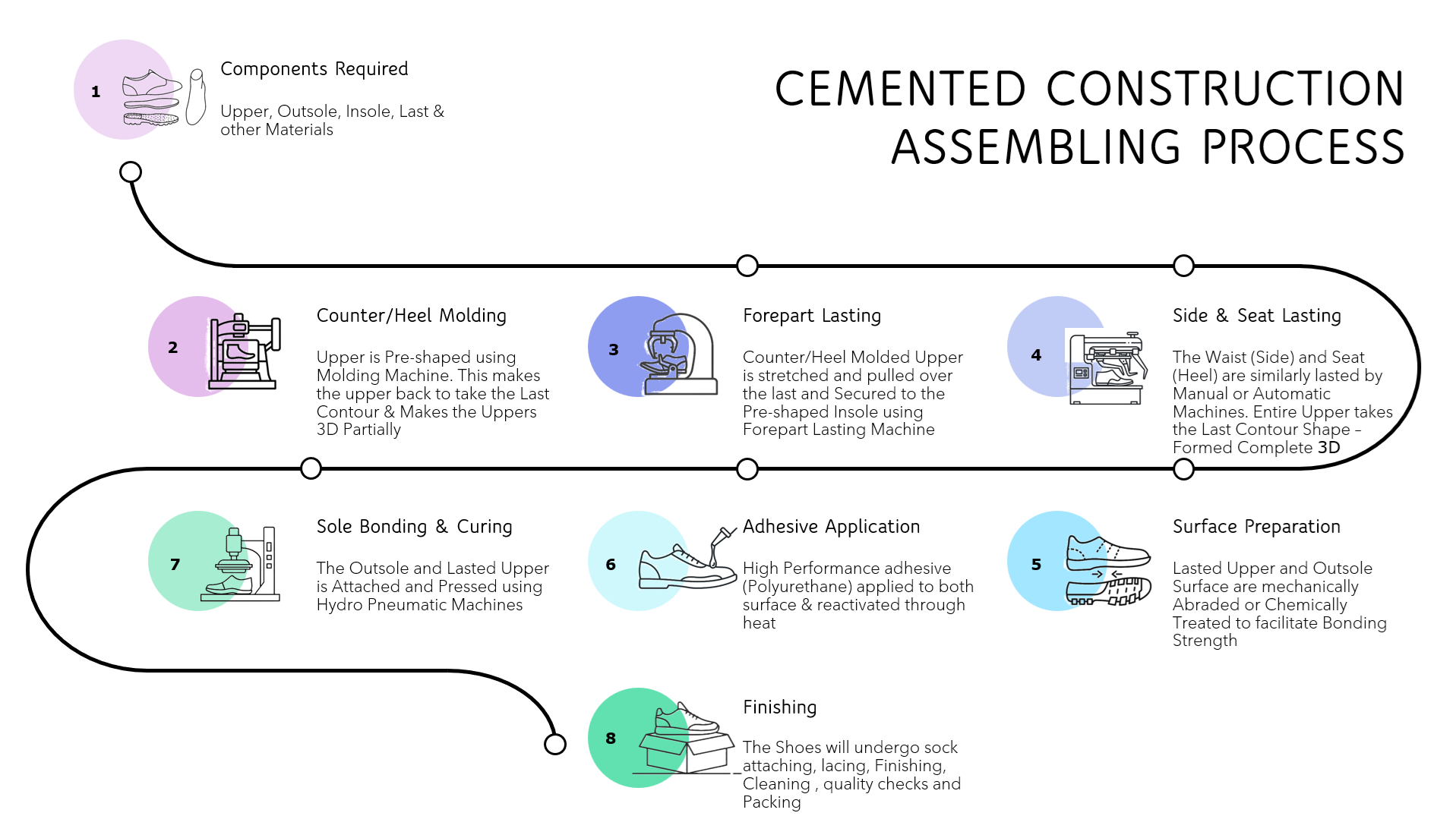
To produce cemented footwear, manufacturers follow a structured sequence of operations with specialized equipment and materials. Below, you can find an overview of the key stages:
Component Preparation
Essential materials include a finished upper (e.g., mesh, leather, or synthetic textiles), outsoles (e.g., rubber, EVA, or TPU or Leather), pre-shaped insoles, footbeds, lasts (foot-shaped molds), and ancillary items such as laces and packaging materials.
Upper Molding
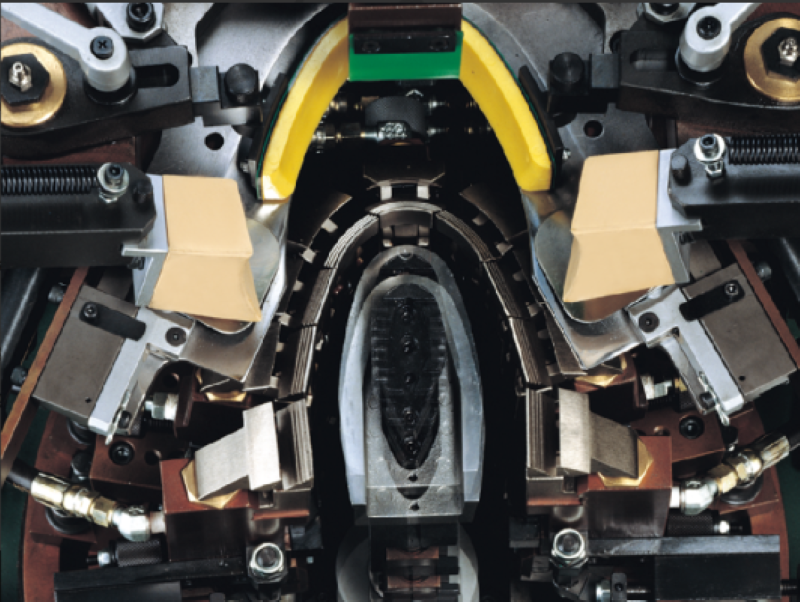
The upper is pre-shaped using heat and cold aluminum molds to activate reinforcements (stiffeners) at the toe and heel. This step transforms the flat upper into a partial three-dimensional form, with precision in back-part molding critical for fit and aesthetic quality.
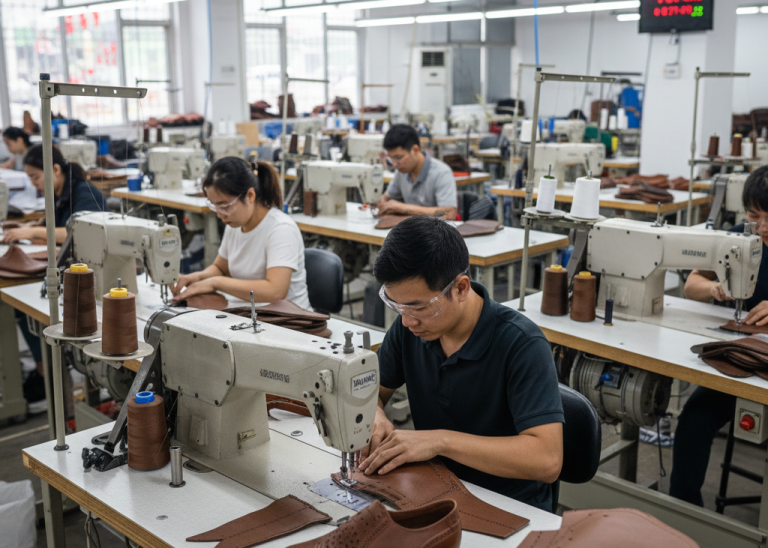
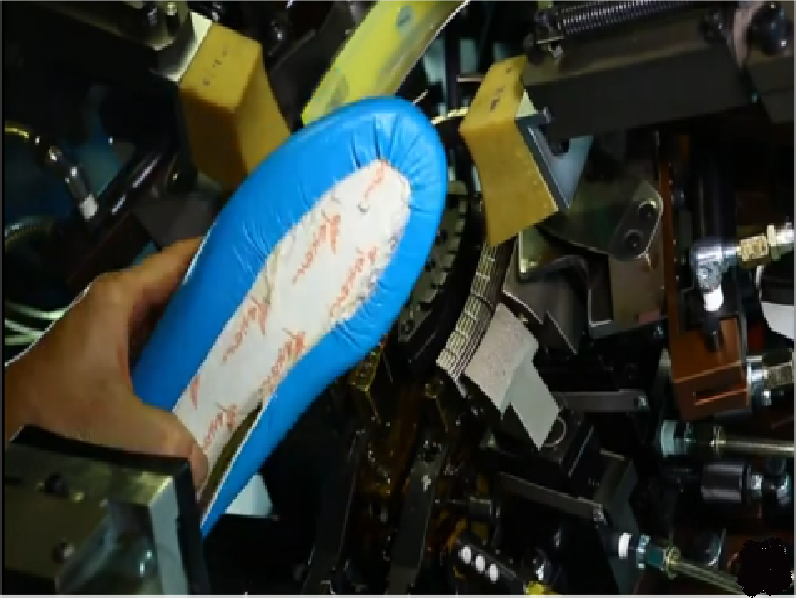
Forepart Lasting
The upper is stretched over the last and secured to the pre-shaped insole using fully automated forepart lasting machines. A margin of approximately 14-16mm is pulled onto the insole with rapid-dry hot melt adhesives, converting the two-dimensional forepart into a three-dimensional contour.

- Seat and Side Lasting: The waist (sides) and seat (heel) are similarly processed using manual or automated machines, ensuring the upper conforms precisely to the last’s shape. Conditioning and heat treatment follow to enhance shape retention, particularly for leather footwear.
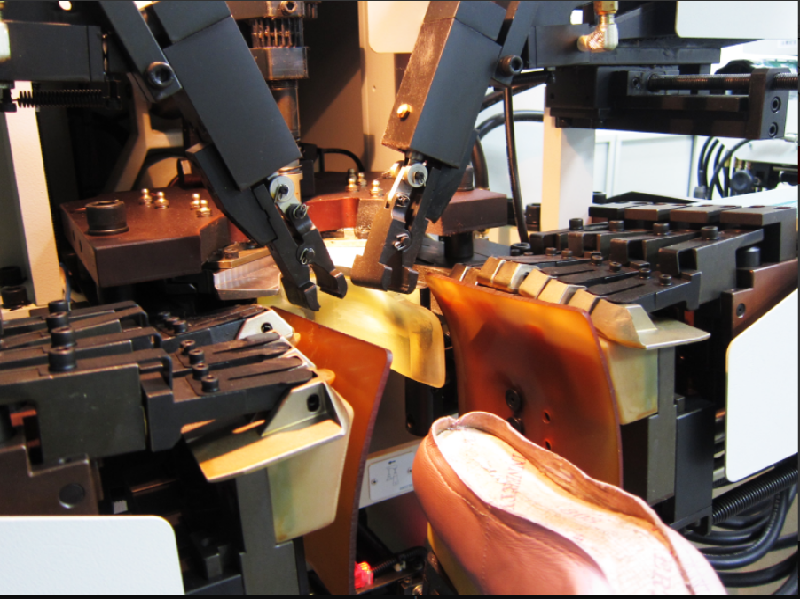


- Assembly and Outsole Bonding:
- Surface Preparation: The lasted upper bottom and outsole are mechanically abraded to improve adhesive grip. Primers or halogenation agents may be applied to synthetic soles to enhance bonding strength.
- Adhesive Application: High-performance adhesives, typically polyurethane-based, are applied to both surfaces and activated through heat or chemical curing.
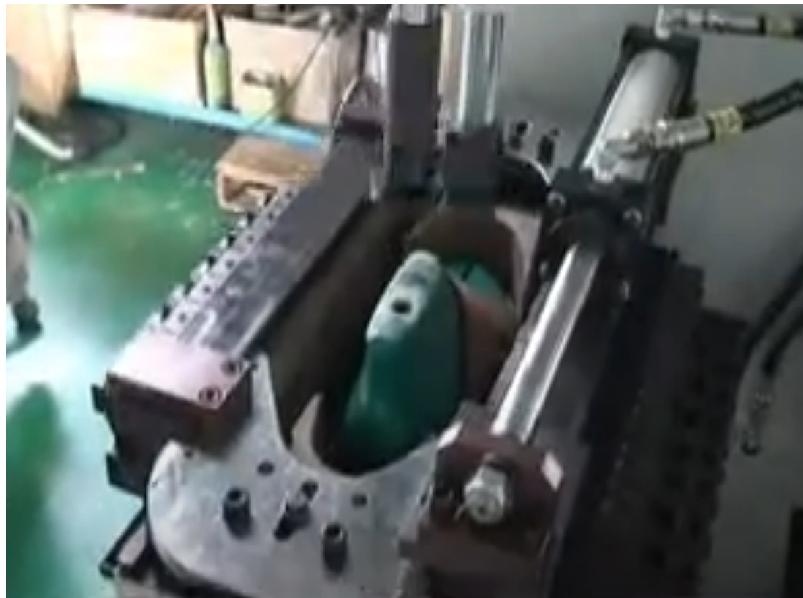
- Sole Bonding: The outsole is aligned and pressed onto the upper using hydro-pneumatic pressing machines, with controlled pressure and dwell time ensuring a uniform bond.
- Curing: Shoes are placed in a cooling tunnel or left at room temperature to allow the adhesive to set fully, enhancing long-term durability and resistance to delamination.
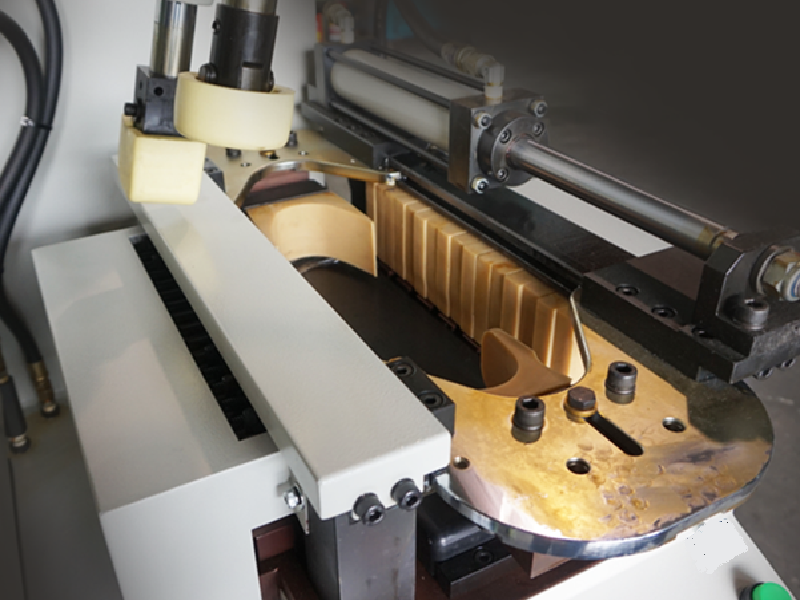


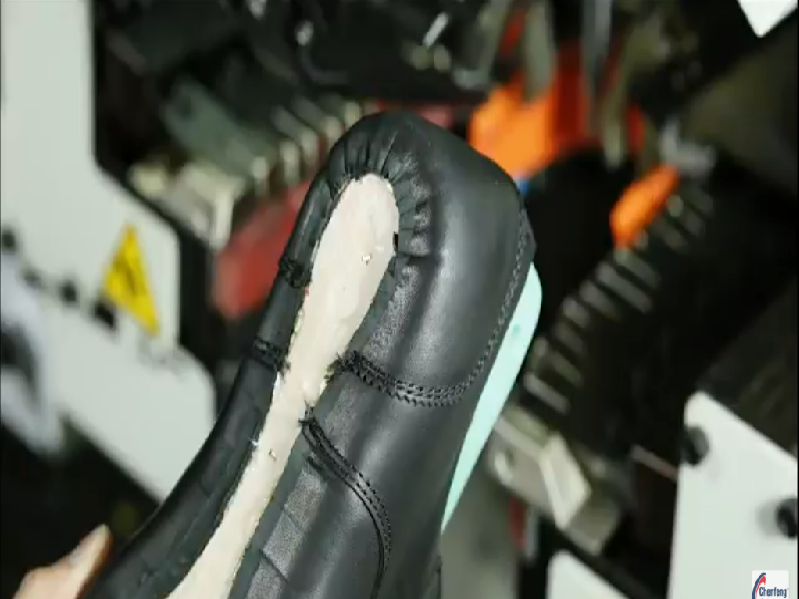
- Finishing: The last is removed, and the shoes undergo, Sock attaching, cleaning, polishing, quality control checks, and packaging.
Historically, lasting was performed manually with nail tacks, but contemporary demand has driven the adoption of advanced machinery to meet market needs efficiently.

4. Materials Utilized in Cemented Construction
The quality and durability of cemented footwear depend on the selection of appropriate materials, as outlined below:
Component | Common Materials |
Upper | Mesh, leather, synthetic textiles |
Insole | Fibreboard, Non Woven, Etc |
Adhesive | Polyurethane (PU) |
Outsole | Rubber, EVA, TPU, Leather, Etc |
These materials are chosen to optimize weight, durability, and comfort, catering to diverse footwear applications from athletic to casual designs.
5. Sustainability and Technological Innovations
Traditional adhesives in cemented construction have raised environmental concerns due to volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. However, the industry is transitioning toward water-based and bio-based adhesives, which offer reduced environmental impact. Additionally, the compatibility of cemented construction with recycled materials, such as rubber outsoles and eco-friendly uppers, positions it as a viable option for sustainable footwear production. Technological advancements, including automated bonding systems, further enhance efficiency by minimizing waste and energy consumption, aligning with global sustainability goals.
6. Conclusion: The Strategic Importance of Cemented Construction
Cemented construction stands as a versatile, scalable, and efficient methodology that underpins a significant portion of the global footwear industry. Its ability to balance production optimization with product durability and design flexibility makes it indispensable for manufacturers. For industry professionals seeking to refine production processes or consumers interested in the craftsmanship behind their footwear, this technique provides critical insights into modern shoemaking practices. Future articles will delve deeper into individual operations to further elucidate the complexities of footwear production.