Beyond the Last’s Surface: A Deep Dive into Hinges, Plates, and Technical Features
In our last post, we explored the shoe last as the foundational blueprint for any shoe, breaking down its anatomy, materials, and crucial role in footwear design. While a last’s shape defines a shoe’s aesthetics and fit, its hidden engineering features are what make modern shoemaking possible.
This post will go beyond the surface to uncover the advanced, yet often overlooked, components of the last: the hinges and bottom plates. These clever mechanisms are the silent champions of footwear production, transforming a static mold into a dynamic tool essential for efficiency, durability, and a flawless final product.
1. Solid vs. Hinged Lasts: A Foundational Choice
Solid Last: The Unyielding Form
A solid last is a single, unmovable piece. It’s the most basic type of last and is typically used for open-style footwear like sandals, mules, or slippers.
- How it Works: The shoe is built directly on the solid form. Once the shoe is completed, the last is simply pulled out through the shoe’s open top.
- Best For: Simple, open footwear where the last can be easily removed without bending or collapsing. Trying to use a solid last for a closed-toe shoe would be difficult and would likely damage the finished product.
The Ingenious World of Last Hinges
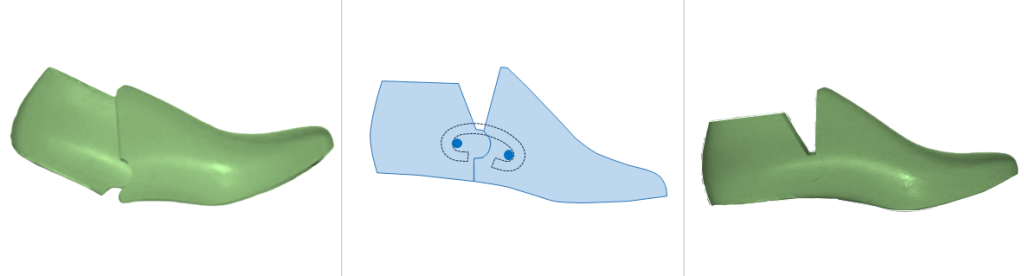
A hinged last is a more advanced and versatile tool. Unlike a solid last, it is made of two or more parts connected by a metal hinge and spring mechanism. This design allows the last to be collapsed, shortened, or otherwise manipulated to make removal from a closed-toe shoe significantly easier.
- How it Works:
After the shoe is fully constructed, pressure is applied to the last, causing it to break or shorten . This reduces the last’s overall length, allowing it to be easily slipped out of the shoe without deforming upper or damaging seams. - Best For: Virtually all closed-toe footwear, including boots, pumps, loafers, and dress shoes.
2. A Closer Look at Different Hinged Lasts and Their Uses
The simple hinged last has evolved into several specialized variations, each tailored for a specific type of shoemaking .
a. Connectional / V-Cut Hinge: This is the most common type. The last is divided into two main parts—a forepart and a backpart—with a “V” cut at the joint. When pressure is applied, the last bends at this cut, shortening its length. This is a general-purpose hinged last used for a wide range of footwear.
b. Slidomatic Hinge: This innovative design is a favourite for certain types of shoemaking, particularly for moccasins and other shoes with a pre-sewn upper. Instead of bending, the two parts of the last slide against each other. The backpart moves slightly upward, shortening the last without a prominent “break” line, which helps maintain the integrity of the upper during removal
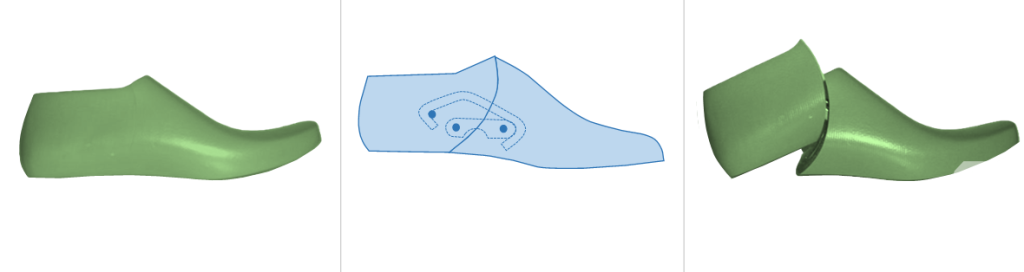
c. Telescopic Hinge: As the name suggests, this type of last works like a telescope, with one part sliding into the other. It’s especially useful for Genuine Handsewn (moccasins) , as it can be collapsed inward to an even greater degree than other hinges, making it easy to withdraw without collapsing the Topline and to insert the last without distorting the topline
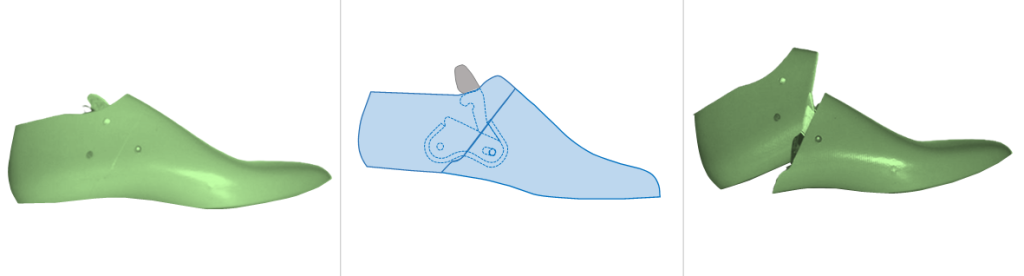
d. Scoop Hinge: A two-part last where a removable “scoop” or cone section is cut from the top of the last’s instep. Removing this piece first collapses the last, making it easier to pull out. This design is often used for High Instep Tall Boots.
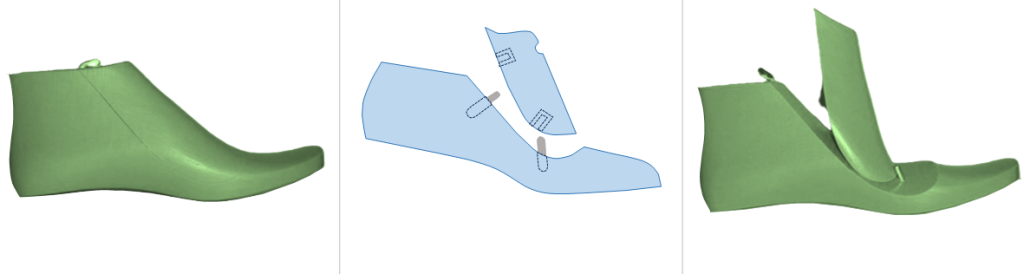
e. Gripper Plated Last: While technically a hinged last, this type is defined by a metal plate on the top. The plate serves a critical function in machine-based shoemaking, particularly injection molding
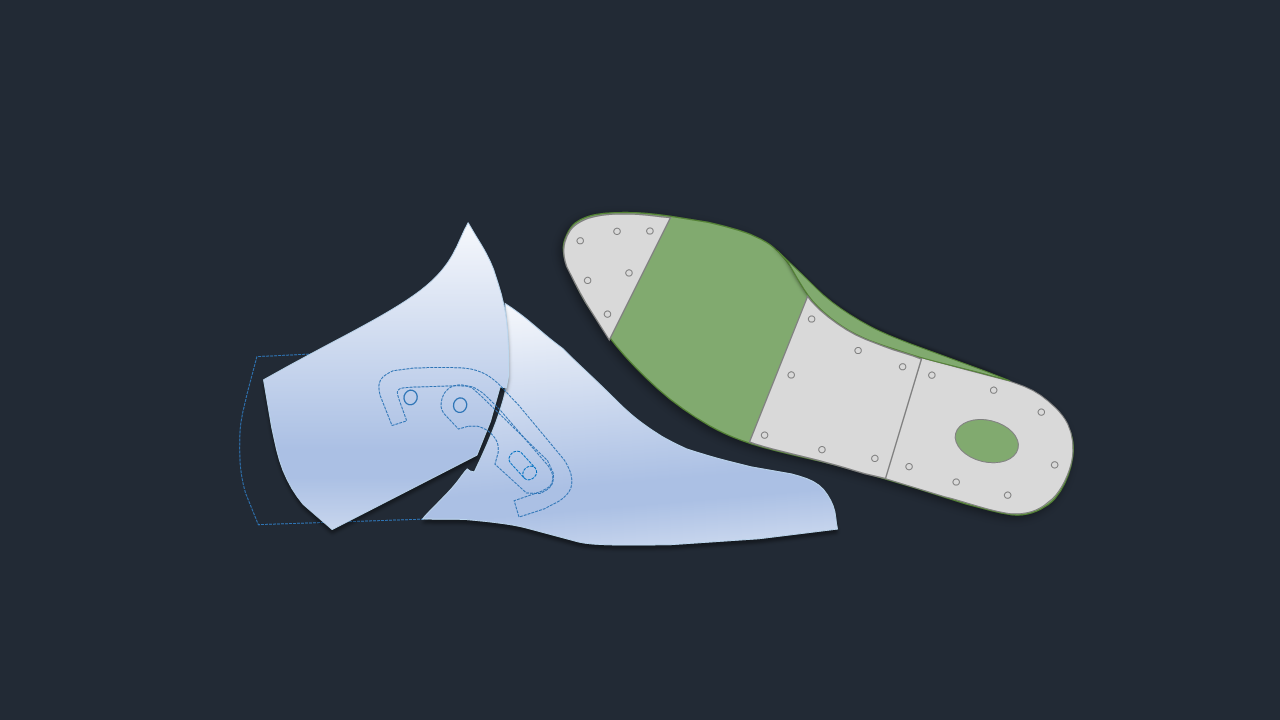
3. Last Bottom Plates
While hinges handle last removal, bottom plates on the underside of the last are what make modern lasting and sole attachment possible. These metal plates—typically made of durable steel or aluminum—are not just for protection; they are functional components that enable high-quality and efficient production.
Here’s a breakdown of the different types of last bottom plates and their critical functions:
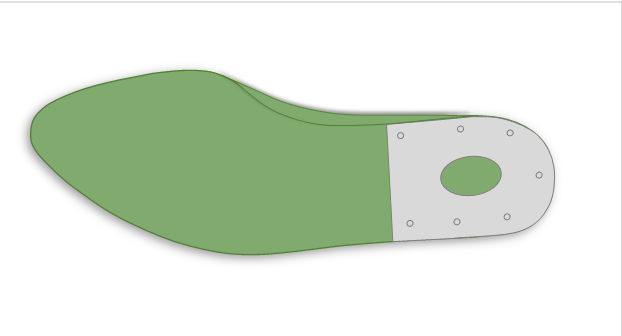
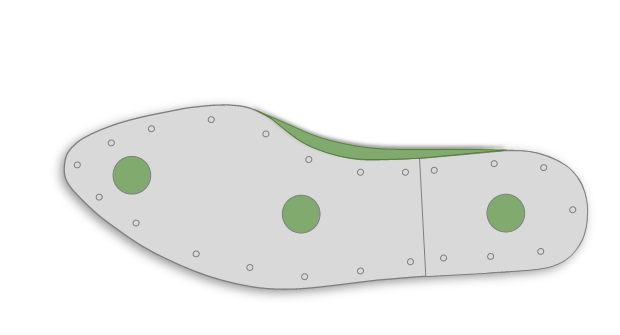
Heel Plate
A metal plate attached to the bottom of the last at the heel. It protects the last from damage during lasting operations where the heel area is hammered or nailed. Most importantly, the hard surface of the plate causes the tips of nails to blunt and curl back into the insole, securing the layers of the shoe without damaging the last itself.
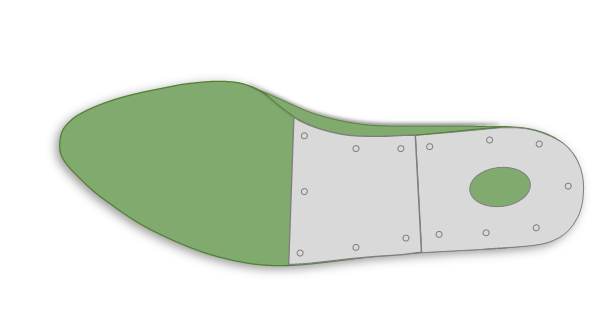
Waist and Toe Plate
- This type extends to cover both the waist and the entire bottom of the toe area. It provides maximum durability and a solid surface for toe lasting machines to pull and secure the upper material. The plate protects the last from the repetitive stress of lasting and from nails used to hold the material in place.
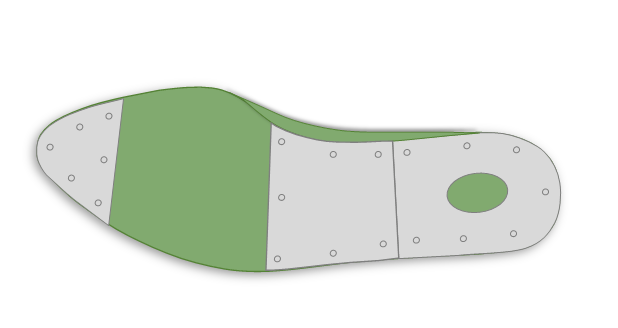
Waist Plate
- This plate runs along the narrow middle section of the last, reinforcing the arch area. The waist is a high-stress point during lasting, and this plate prevents the last from warping under pressure, ensuring a clean, consistent arch line in the finished shoe.
Full Plate
- This single, continuous plate covers the entire bottom surface of the last. It provides the highest level of durability and precision, serving as a stable base for the lasting machine’s grippers.
This type is crucial for highly automated processes like injection molding, where the sole is directly molded onto the upper, requiring a perfectly flat and rigid surface for the machinery to function correctly.
4. The Synergy of Design: How Hinges and Plates Work Together
This final section can tie everything together, emphasizing that these components work in unison.
The hinge allows for the last to be removed, while the bottom plates ensure the last maintains its precise shape throughout thousands of cycles in a factory setting.
This synergy is what enables both high-quality craftsmanship and mass production