Footwear Manufacturing Insights – Last Form as a Construction Aid & Elastic Gusset Stitching
Reading Time : 5 Minutes
In footwear pattern engineering, the last form and elastic gusset construction play a decisive role in achieving accurate fit, functional comfort, and clean finishing. These elements directly influence how well a shoe performs during wear and how consistently it can be produced in a factory environment.
The following insights are extracted and interpreted from traditional pattern-modelling practices commonly used in boot and shoe development. Though traditional, these techniques remain highly relevant in modern footwear engineering.
Using the Last Form as an Aid to Construction
The last form is not only a shaping tool but also a critical construction reference during pattern development. By physically manipulating the last, pattern engineers can identify key reference points without relying solely on numerical measurements.
This approach improves accuracy, repeatability, and alignment between the pattern and the actual last geometry.
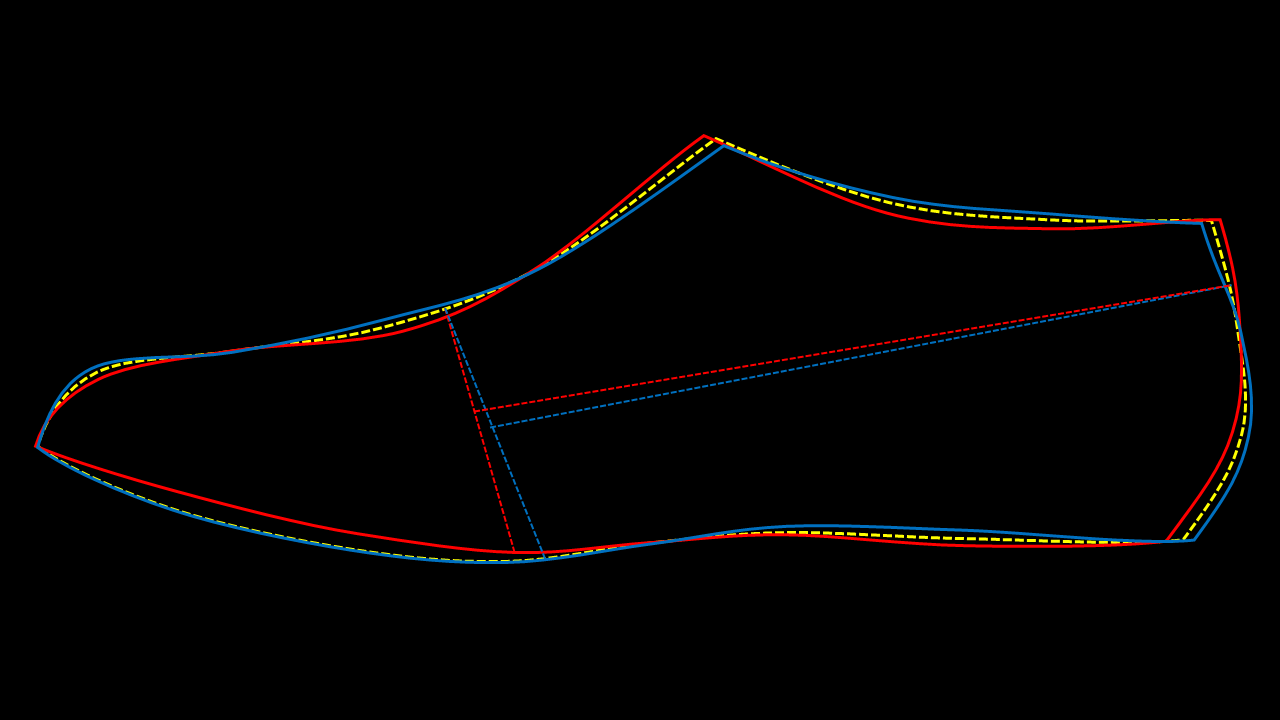
Principle of Folding the Last
By folding the toe of the last backward, with the toe pointing toward the centre of the back line, important construction references become visible:
- Back Line (A):
Acts as the primary vertical reference for the last. - Spring Point Identification:
The spring point becomes visible by observing where the toe aligns relative to the back line. - Seat Line (B):
When taken approximately 1 cm beyond the spring point, the seat line allows suitable allowances, particularly useful for oversized or special-purpose lasts.
This folding method converts the last into a practical measuring aid rather than a passive shape.
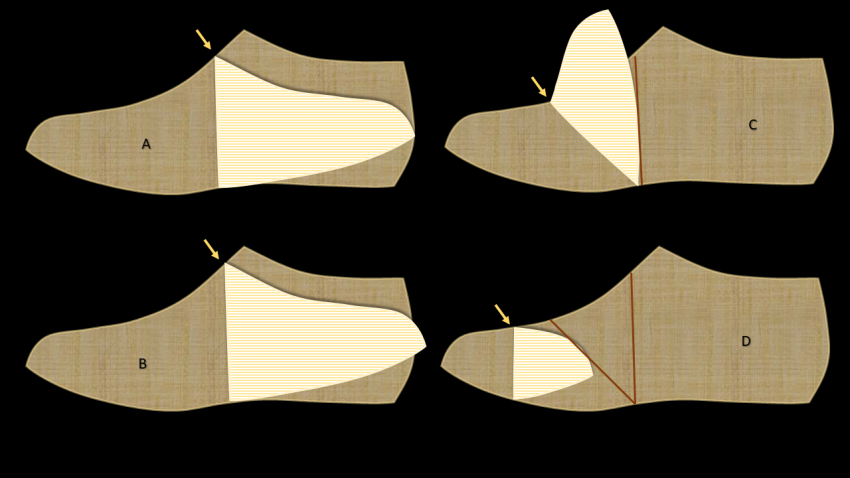
Identification of Key Construction Points
Different folding positions of the toe reveal specific reference points essential for pattern layout:
- Spring Point (C):
When the toe is folded to form a right angle with the break line, the spring point is clearly established. - Cap Line Position (D):
When the toe is folded further backward toward the centre of the break line of the golosh point, the correct cap line position becomes visible.
These folded positions provide geometric certainty, reducing dependency on estimated dimensions and improving pattern consistency.
Manufacturing Value
Using the last form as a construction aid enables pattern makers to:
- Accurately locate spring and cap reference points
- Improve alignment between pattern geometry and last shape
- Reduce trial-and-error during early development stages
- Achieve better first-sample accuracy
This technique is especially valuable during new last development and boot pattern engineering.
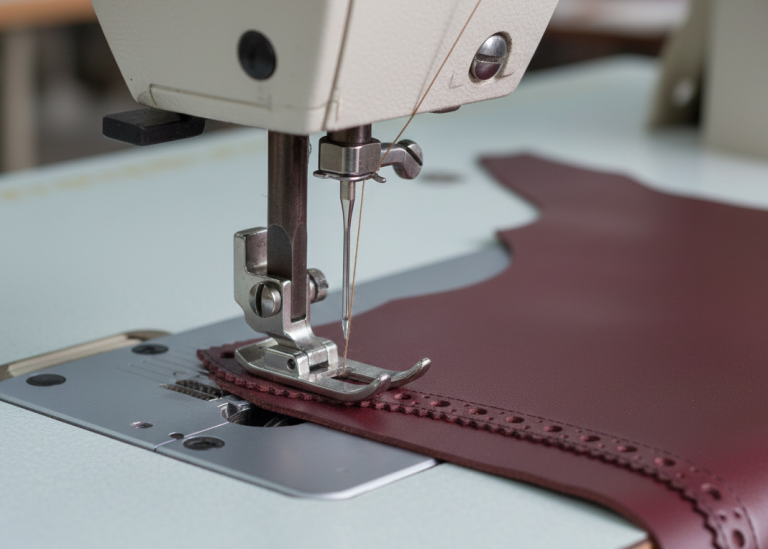
Stitching-In of Elastic Gussets
Elastic gussets are widely used in footwear—especially in boots and slip-on styles—to improve flexibility, ease of entry, and wearer comfort. However, incorrect proportioning or stitching technique can lead to uneven edges and distortion.
Proper construction logic is essential to maintain both function and appearance.
Width Relationship Between Saddle and Elastic
For correct elastic gusset construction:
- The saddle piece must be wider than the elastic
- Cutting both components to the same width often results in uneven or stepped edges after stitching
To avoid this issue, the edge-folded saddle part should overlap the elastic slightly at the side.
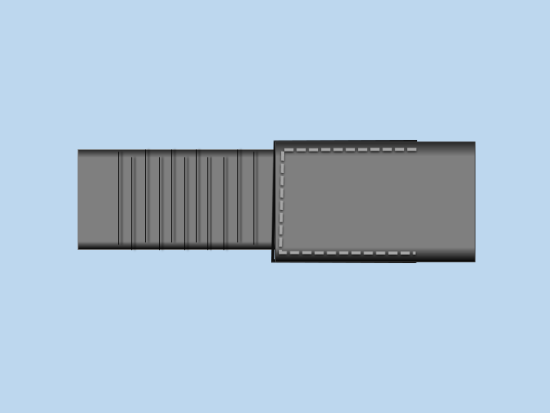
Construction Logic
The saddle overlap serves multiple functional purposes:
- Compensates for elastic stretch during wear
- Maintains a clean and uniform stitched edge
- Prevents distortion during repeated flexing
- Improves both visual appearance and durability
This small but critical detail is often overlooked and becomes a common source of quality complaints.
Production Advantage
Correct elastic gusset stitching delivers clear manufacturing benefits:
- Prevents edge distortion
- Ensures aesthetic consistency across pairs
- Enhances long-term functional performance
- Reduces rework and rejection in the stitching line
Manufacturing Value
By combining proper vamp lining fold-line control with precise spring adjustment techniques, footwear manufacturers can:
- Achieve consistent fit in structured uppers and boots
- Reduce pattern redevelopment time
- Improve repeatability during sampling and bulk production
Posts you may like
Conclusion
By combining last-form folding techniques with correct elastic gusset stitching principles, footwear manufacturers can significantly improve:
- Pattern accuracy
- Construction quality
- Fit consistency
- Production reliability
These traditional yet highly effective methods remain essential tools for pattern engineers, especially when developing boots and elastic-sided footwear. Mastery of such fundamentals separates average construction from truly professional footwear engineering.