Guide Marking in Footwear Manufacturing: Complete Technical Guide to Methods, Materials, and Modern Innovations
Reading Time : 8 – 10 Minutes
Introduction
Guide marking is a fundamental preparatory process in footwear manufacturing that ensures shoe components are accurately positioned before stitching, assembling, folding, bonding, or attaching. Although it may appear to be a small operational step, guide marking has a major influence on visual consistency, seam integrity, bonding strength, and overall production efficiency.
In today’s competitive footwear industry, where factories in China and Vietnam lead high-volume production, guide marking has evolved from basic chalk lines to advanced solutions such as UV marker pen technology. These innovations eliminate post-cleaning, improve operator accuracy, and significantly reduce quality risks.
This blog provides a complete technical perspective on guide marking — covering traditional methods, tool and ink management, maintenance discipline, and the latest UV-based marking systems shaping modern mass production.
What Is Guide Marking?
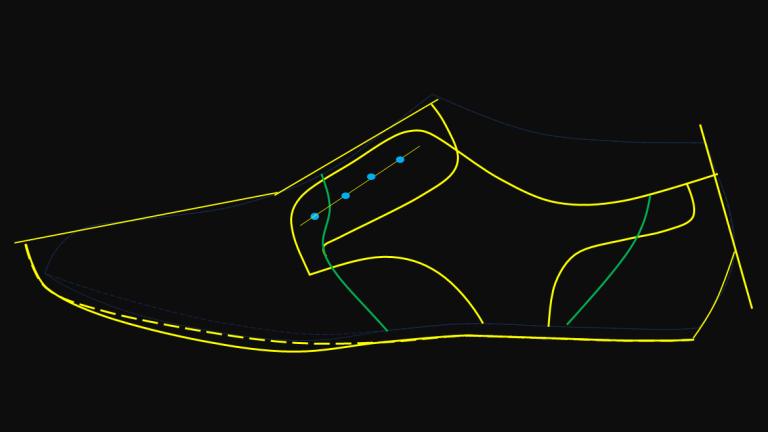
Guide marking is the process of applying visual or physical reference lines on footwear components to indicate:
- Stitching paths
- Fold lines
- Bonding and cementing zones
- Alignment points for lasting and assembly
- Decorative stitch and trim positions
These guides support operators across multiple stages, including:
- Upper stitching
- Toe puff and counter attachment
- Lasting alignment
- Sole bonding
- Decorative operations
In high-volume environments, guide marking functions as a process control tool, ensuring repeatability and reducing dependence on individual operator judgment.

Why Guide Marking Is Critical to Footwear Quality
Accurate guide marking directly affects both aesthetic quality and functional durability. When guide marks are unclear, inconsistent, or incompatible with materials, the following issues commonly occur:
- Uneven or crooked stitch lines
- Misaligned bonding zones causing weak adhesion
- Decorative elements placed asymmetrically
- Stress concentration near incorrect seams or joints
- Surface cracking or premature material failure
These defects translate into:
- Higher rejection and rework rates
- Increased labor and material costs
- Customer complaints and brand risk
For this reason, leading manufacturers treat guide marking as an upstream quality gate, not merely a preparation task.
Traditional Guide Marking Methods – Technical Overview
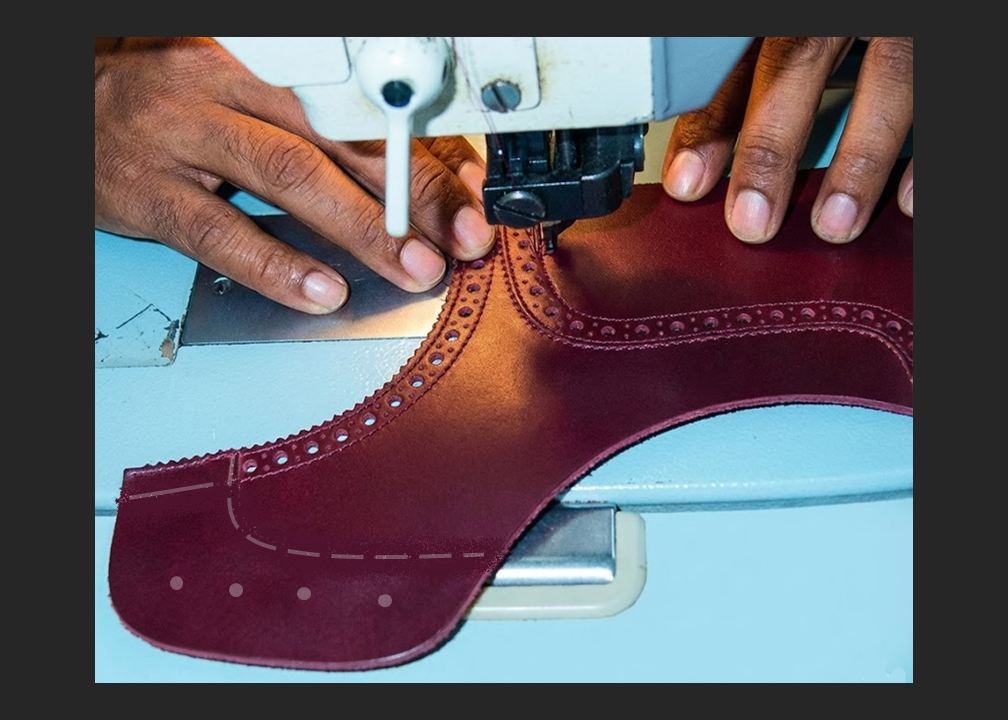
1. Hand Guide Marking
Hand marking remains common in sampling rooms, development centers, and small-batch production. Operators use chalk, pencils, or ink pens to apply guide lines manually.
Technical strengths
- High flexibility for rapid design changes
- No equipment investment
- Suitable for prototypes and short runs
Technical limitations
- Accuracy varies by operator skill
- Inconsistent line thickness and placement
- High risk of variation in mass production
- Greater chance of visible residue on finished uppers
2. Template-Based Guide Marking
Templates made from plastic, hardboard, or metal are used to standardize marking positions. The template defines the geometry while the operator traces the guide lines.
Operational advantages
- Improved repeatability versus freehand marking
- Better control over decorative stitch placement
- Moderate investment cost
Technical risks
- Template edge wear leads to creeping inaccuracies
- Ink buildup contaminates future markings
- Misalignment during placement creates systematic defects
- Requires strict cleaning and inspection cycles
Posts you may like
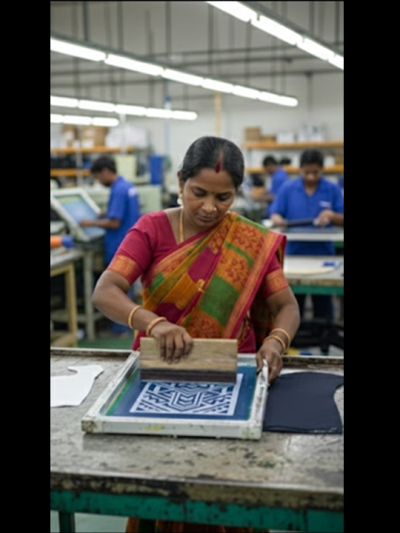
3. Screen Printing of Guide Lines
Screen printing transfers guide lines onto uppers using ink and a fine mesh stencil. It is widely used in mass production because of its consistency.
Technical advantages
- Uniform markings across large batches
- Excellent for decorative and complex patterns
- Reduced operator dependency
Operational challenges
- Ink viscosity must be controlled
- Drying time affects takt time
- Screens require frequent washing
- Risk of ink bleeding on porous materials

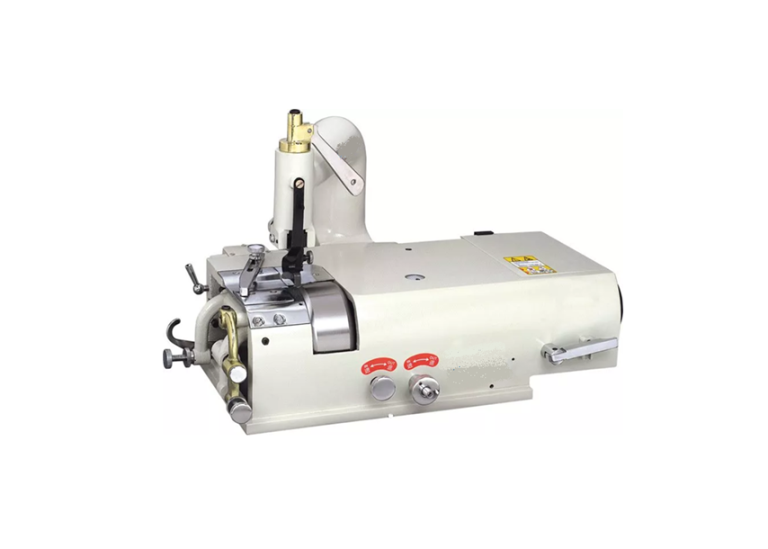
4. Machine-Aided Guide Marking
Fixed and hinged marking machines automate the transfer of guide lines using templates, pads, or ink rollers.
Technical strengths
- High repeatability
- Reduced human error
- Suitable for continuous production lines
Maintenance requirements
- Regular calibration of alignment plates
- Replacement of worn rollers
- Monitoring ink transfer consistency
- Periodic validation against master patterns
5. Press Knife Guide Marking
Press knives create controlled indentations on the surface instead of applying ink. These indentations act as tactile and visual guides.
Key advantages
- No ink contamination
- No risk of smudging
- Ideal for light-colored or sensitive materials
Technical limitations
- Indentations may fade if the upper stretches
- Not suitable for very soft or spongy materials
- Poorly designed knives can permanently damage surfaces

Tools, Inks, and Materials: The Hidden Determinants of Success
One of the most overlooked areas in guide marking is material compatibility. Many marking failures originate not from the method, but from incorrect ink, poor tool design, or weak maintenance discipline.
Press Knives and Templates – Design Discipline
Press knives and templates must be engineered with precision:
- Edges should mark without cutting fibers
- Contact pressure must be controlled
- Surface finish must avoid scratching coatings
- Alignment references must be repeatable
Poor tool design leads to:
- Permanent surface scars
- Distorted grain patterns
- Inconsistent marking depth
- Long-term aesthetic defects

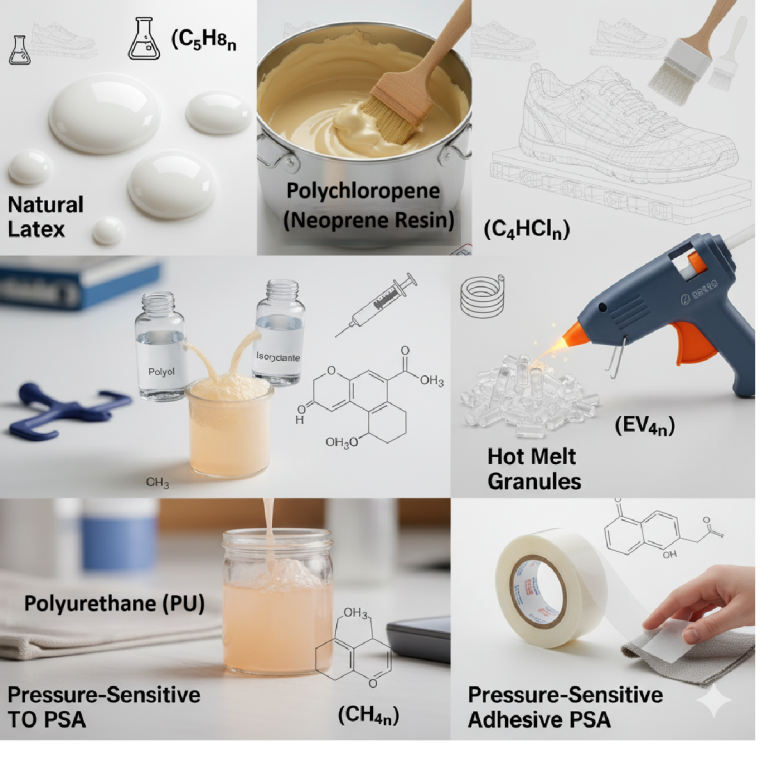
Ink Selection – Technical Requirements
Inks used for guide marking must meet four critical criteria:
- Visibility during operation – clear enough for stitching and assembly
- Chemical compatibility – no reaction with finishes, dyes, or coatings
- Controlled penetration – must not migrate deep into fibers
- Safe removability – should clean off without leaving shadows
Light petroleum-based inks are commonly preferred because they:
- Evaporate safely
- Meet industrial safety standards
- Can be removed with mild cleaners
- Reduce risk of long-term staining
Cleaner Compatibility and Surface Safety
Incorrect cleaning practices cause more damage than marking itself. Effective factories follow strict protocols:
- Always test cleaners on scrap uppers first
- Avoid aggressive solvents that attack finishes
- Use gentle detergents or specialty marking removers
- Apply minimal mechanical rubbing to avoid grain damage
Over-cleaning often results in:
- Breakdown of protective coatings
- Discoloration halos
- Surface dulling
Equipment Cleaning and Maintenance
Consistent guide marking requires disciplined maintenance:
- Daily cleaning of marking heads and rollers
- Weekly inspection of templates and press knives
- Replacement of worn components before accuracy degrades
- Scheduled calibration of machines
Neglecting maintenance leads to:
- Progressive misalignment
- Ink buildup and blotting
- Unnoticed drift in marking position
- Systematic quality defects across batches
The Breakthrough: UV Marker Pen Technology for Guide Marking
What Is UV Guide Marking?
UV marker pens apply invisible guide lines that become visible only under ultraviolet light. Under normal lighting, the marks remain unseen on the component surface.
his technology is now widely adopted in Chinese and Vietnamese mass-production footwear factories, especially in:
- Sports footwear
- Fashion shoes
- Export-oriented premium lines
Source: UV Refill
How the System Works
- Operator applies guide lines using a UV marker pen.
- Lines remain invisible in normal light.
- UV lamps installed near stitching or assembly stations illuminate the marks.
- Operators follow the glowing guides with absolute precision.
- Finished uppers leave the line with zero visible residue.
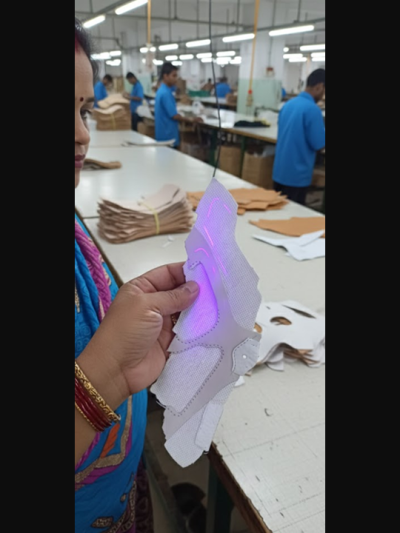

Technical Advantages of UV Guide Marking
1. Elimination of Post-Cleaning
UV marks do not appear under normal light, so no erasing or cleaning is required after stitching or bonding. This removes an entire operation from the process flow.
2. Cleaner and Safer Production
No chalk dust, no ink transfer, and no solvent use — resulting in:
- Cleaner workstations
- Lower chemical exposure
- Improved workplace safety
3. Superior Operator Visibility
Under UV light, guide lines are:
- Highly contrasted
- Easy to follow
- Visible even on dark, glossy, or patterned materials
4. Protection of Premium Surfaces
Luxury and export brands prefer UV marking because:
- There is zero risk of visible stains
- No surface abrasion from cleaning
- No chemical interaction with finishes
5. Mass Production Efficiency
Factories in Vietnam and China report:
- Reduced rework rates
- Faster stitching and assembly speed
- More consistent visual appearance
- Lower overall cost of quality
Integrating Guide Marking into Quality Systems
To achieve stable results, guide marking must be embedded into the factory Quality Management System (QMS).
Recommended controls include:
- Defining guide marking as a critical control point
- Standardizing methods by product category
- Creating SOPs for:
- Ink selection
- Template maintenance
- UV lamp calibration
- Including guide marking checks in:
- Line audits
- Process capability reviews
- New material trials
Best Practices for High-Performance Guide Marking
Leading footwear factories apply these principles:
- Select marking method based on material sensitivity and volume
- Validate inks and cleaners before bulk use
- Train operators in visual alignment discipline
- Maintain tools and machines proactively
- Introduce UV guide marking for:
- Premium lines
- Light-colored uppers
- High-precision assemblies
Conclusion
Guide marking has evolved from a simple manual operation into a strategic technical process that underpins footwear quality. Traditional methods such as hand marking, templates, screen printing, and press knives still have their place, but modern production increasingly depends on UV marker pen technology to achieve higher cleanliness, accuracy, and efficiency.
For footwear manufacturers aiming at global standards, guide marking is no longer optional — it is a core enabler of consistency, durability, and brand excellence.